



-
- Free Word Search




In medical facilities and hospitals, there are many devices and equipment used to treat patients and protect their lives. In order for these to operate stably, it is extremely important to secure a power supply. Stopping equipment due to unexpected power outages or other power problems puts patients at risk, so this must be avoided.
For this purpose, UPS (uninterruptible power supply) plays a very important role.
This article provides a detailed explanation of the typical devices and equipment to be backed up in hospitals and medical facilities, including medical electrical equipment such as dialysis treatment machines, operating lights, and equipment involving data management, as well as the UPS suitable for each and the performance and functions required.
* When used in medical electrical equipment that directly affects human life, special consideration is required for operation, maintenance, and management.
We make proposals in accordance with the Japanese Industrial Standards "Safety Standards for Electrical Equipment in Hospitals (JIS T 1022)" and the Japan Electrical Manufacturers' Association document "Technical Guidelines for the Application of Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) to Medical Institutions (JEM-TR 233)," so please feel free to consult us. Pleasesee Section 4 for details.
Medical facilities and hospitals use a large number of electrical medical devices that are involved in the diagnosis, treatment, and life of patients. For example, these include monitoring systems essential to maintaining the lives of patients in intensive care units (ICUs), as well as devices that directly support the lives of patients, such as artificial ventilators and dialysis treatment equipment. Ultrasound diagnostic equipment is also an example of electrical medical equipment. These devices are essential for accurately understanding the health status of patients and providing prompt and appropriate treatment.
In hospitals and medical facilities, many patients are diagnosed and treated every day. Especially in operating rooms and intensive care units (ICUs), where high-risk equipment is used, even a small power problem can cause the equipment to stop working, putting the patient at risk. Even if the equipment does not stop working, it can still cause damage to medical electrical equipment.
UPS is an extremely important device that supplies power when power outages and other power problems occur, playing a role in reducing these risks.
*If this product is used in medical electrical equipment that directly affects human life, special consideration must be given to operation, maintenance, and management. Please consult with us.
The appropriate size UPS must be selected depending on the size of the medical electrical equipment, but it is often around 10kVA to 20kVA.
In the case of artificial dialysis treatment machines, depending on the size of the hospital, multiple dialysis treatment machines are used, such as 10 to 15 machines. The output capacity [kVA] of the UPS is basically the number of rated capacity [kVA/unit] of the dialysis treatment machines, but inrush current must also be taken into consideration.
Backup time is often about 10 minutes, as it is often used in conjunction with private power generation equipment, to make up for the 40 seconds it takes for the generator to start up. If a generator cannot be used in conjunction with the power generation equipment, a backup of several tens of minutes to several hours is required until power is restored in the event of a power outage or other power problem.
Medical electrical equipment such as artificial dialysis treatment machines is equipment that cannot be allowed to stop at any time. In the event of a power outage or other emergency, it would be pointless if the UPS that supplies power to medical electrical equipment were to break down.
With a parallel redundant type UPS, you can rest assured that even if one UPS fails, the other UPS will continue to supply power.

It is important that medical electrical equipment such as artificial dialysis treatment machines be supplied with power without momentary interruption during a power outage. For example, if the power supply is cut off even for an instant during a power outage, and the medical electrical equipment stops functioning or is no longer able to function normally, it could put patients at risk.
It is very important to select a UPS that can supply power without interruption, such as
Double Conversion Online or Parallel Processing.
*If this product is used in medical electrical equipment that directly affects human life, special consideration must be given to operation, maintenance, and management. Please consult with us.
If the operating lights go out due to a power outage, the surgery cannot be continued, and the patient is put at risk. Therefore, a UPS is required to supply power so that the lights can continue to be on even if a power outage or other power problem occurs during surgery.
In the case of surgical lights, they are often less than 1kVA.
On the other hand, if there is no private power generation equipment, a long backup time is required, such as 30 to 180 minutes until the end of the surgery.
In the case of surgical lights, even if a power outage occurs, power must be supplied until the surgery is safely completed. In cases where the surrounding environment does not allow for the installation of a private power generating facility, it is necessary to select a UPS that can provide long-term backup, such as 30 to 180 minutes.
A UPS that provides long-term backup requires a large battery, and the UPS battery panel often becomes large in volume. At the same time, because space within a hospital is limited, a compact and space-saving UPS is also required.
A UPS equipped with lithium-ion batteries can provide long-term backup while saving space at the same time.
![Volume/Capacity Comparison [Lead UPS - Lithium-ion UPS]](https://data.wovn.io/ImageValue/production/660a0f3eff2fba0083c85498/en/9b88433abf906cf9713172c94b05585a/case_img_132_capture_2.png) ▲Comparison of volume and capacity [Lead UPS - Lithium-ion UPS]
▲Comparison of volume and capacity [Lead UPS - Lithium-ion UPS]
The reason why these facilities require UPS is because losing access to medical data or losing that data can have a detrimental effect on the life and health of patients.
For example, if an electronic medical record system becomes inaccessible due to a power outage or other power problems, doctors will not be able to access the patient's important medical information, which could result in delays in diagnosis and treatment. Data loss also means that patients' treatment histories and test results cannot be accessed, making it difficult to provide appropriate, ongoing treatment.
To avoid these risks, a UPS is essential.
The appropriate size UPS must be selected depending on the type and scale of the equipment, but in most cases 1kVA to 3kVA, or at most 5kVA, will be sufficient.
The backup time is about 10 minutes when used in conjunction with private power generation equipment to make up for the 40 seconds it takes for the generator to start up. If a generator cannot be used in conjunction with the power generation equipment, a backup of several tens of minutes to several hours is required until power is restored in the event of a power outage or other power problem.
UPS devices must be small and space-saving to be used in the limited space within a hospital or next to testing equipment. A UPS with lithium-ion batteries can save more space than a lead-acid battery UPS.
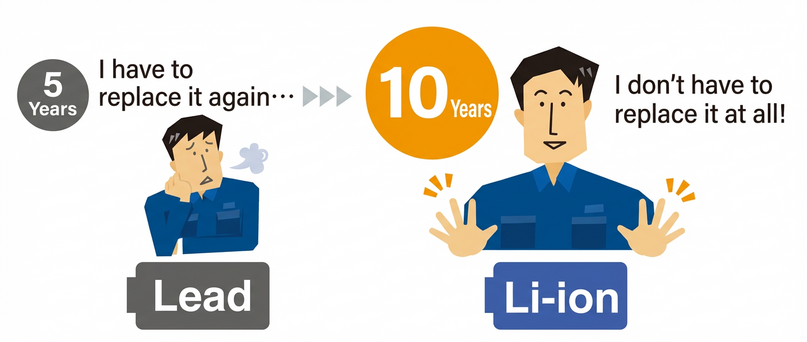
A lithium-ion battery UPS with a battery life of 10 years* reduces the number of battery maintenance requirements compared to lead-acid batteries, which have a battery life of 2 to 5 years, reducing the burden of managing the UPS.
 >
>
*When the ambient temperature is 25°C.
please
The "Safety Standards for Electrical Equipment in Hospitals (JIS T 1022)" and the "Technical Guidelines for Applying Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) to Medical Institutions (JEM-TR 233)" are subject to revision, so please be sure to check the latest original texts.
As you may know, there is the Japanese Industrial Standard "Safety Standards for Electrical Equipment in Hospitals (JIS T 1022)". This standard specifies the safety standards and facility methods for medical grounding, non-grounding wiring, and emergency power sources for electrical equipment installed in hospitals and clinics to ensure the safety of medical electrical equipment. Next, the Japan Electrical Manufacturers' Association document "Technical guidelines for applying Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) to medical institutions (JEM-TR 233)" shows standards, points to consider, and equipment handling when applying UPS to medical institutions (hospitals, etc.) with the aim of preventing accidents caused by power outages in medical institutions. To apply UPS to medical institutions, it is necessary to understand these safety standards and technical guidelines.
This article provides an overview of the "Technical guidelines for applying uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to medical institutions (JEM-TR 233)".
The "Safety Standards for Electrical Equipment in Hospitals (JIS T 1022)" was revised in 2018 to change "instantaneous special emergency power supply" to "uninterruptible emergency power supply," and the definition was also revised. The technical guidelines (JEM-TR 233) aim to prevent accidents caused by power outages in medical institutions, and outline standards, points to consider, and equipment handling when applying UPS to medical institutions (hospitals, etc.).
UPS is used in a wide range of fields, including as a backup power source for computers. However, when it comes to using UPS in medical institutions, safety is a major consideration, and catalogs and instruction manuals state that they should not be used in medical institutions that directly involve human life without special consideration, and that if they are to be used, the manufacturer should be consulted. Our catalogs and instruction manuals are also created in accordance with this guideline.
However, this does not mean that the product cannot be used in medical devices. If you consult with us, we will provide a detailed product explanation and discuss the specifications to help you select the product.
According to JIS T 1022,
(1) An emergency power source is a general term for a power source that automatically supplies power when commercial power is interrupted. (Note: This is different from the "emergency power source" defined in the Fire Service Act.) Emergency power sources are classified as "general emergency power sources," "special emergency power sources," and "uninterruptible emergency power sources," and are defined as follows:
Additional information: Private generating equipment that constitutes an emergency power source includes equipment that has a 10-second or 40-second start-up time that is certified by the Japan Internal Combustion Power Generation Equipment Association.
(2) Medical electrical equipment means an electrical machine or device that has an attachment part, that transmits and receives energy between a patient, that provides energy to a patient, or that detects energy from a patient.
(3) Classification and names of medical electrical equipment The classifications are life support equipment, surgical equipment, diagnostic monitoring equipment, therapeutic equipment, and others.
Supplementary explanation: Advanced electrical medical equipment such as MRI and CT scanners are equipped with computer systems, and in the event of a power outage it takes a long time to restart the systems, so they often require an uninterruptible emergency power source.
Ensuring a power supply is essential in the event of natural disasters such as earthquakes and typhoons. To achieve this, first of all, a power generating facility is required that can generate power even if the commercial power source of the power company is blacked out for a long period of time. In addition, the quality of the power (voltage fluctuations, momentary interruptions, etc.) to the special emergency power load and the uninterruptible emergency load is important, and it is necessary to consider the application of private power generating facilities and UPS depending on the importance of the load.
JIS T 1022 stipulates that "circuits of the following medical electrical equipment, etc., that must be powered without interruption (power source with guaranteed continuity of AC power) when commercial power is interrupted, must be provided with an uninterruptible emergency power supply," and specifies "the following medical electrical equipment" as "medical electrical equipment that requires uninterruptible power supply (power source with guaranteed continuity of AC power)" and "operating lights." It states that UPS is applied in such cases in combination with private power generation equipment. Furthermore, it states that the storage battery of Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) must be able to supply power to a load continuously for 10 minutes or more without charging. For private power generation equipment, private power generation equipment that establishes voltage in 40 seconds or less or 10 seconds or less must be used, and must be able to operate continuously for 10 hours or more.
(1) Single-phase two-wire output type Output capacity (0.35kVA to 20kVA)
You can choose the voltage (100V, 200V), retention time (up to 180 minutes), and battery type (lead-acid battery or lithium-ion battery).
(2) Three-phase, three-wire output type Output capacity (5 kVA to 300 kVA)
Voltage (200V, 400V), retention time (maximum 180 minutes)
(3) For both single-phase output type and three-phase output type, there are also UPSs with a parallel redundant system that offers higher reliability.
(4) Set product combining UPS and private power generation equipment Output capacity (3kVA to 200kVA)
We provide a one-stop service to propose the optimal combination for your facilities and equipment.
If you are using this product in the following types of equipment, special considerations will be required for operation, maintenance, and management. Please consult with us.
Supervisor: Dr. Kiyotaka Izumiya, Senior Technical Advisor, Sales Department SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
release date: