



-
- Free Word Search




The electricity sent from the power company is called commercial power. Passive Standby is a method in which commercial power is supplied directly to the equipment.
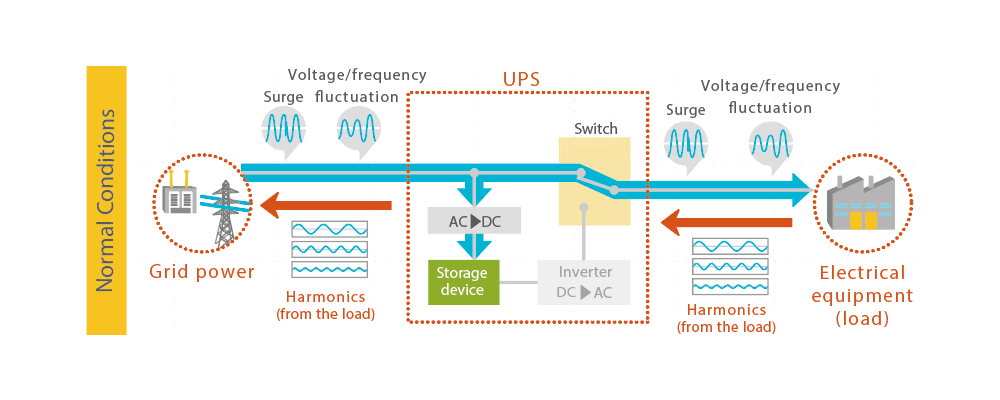
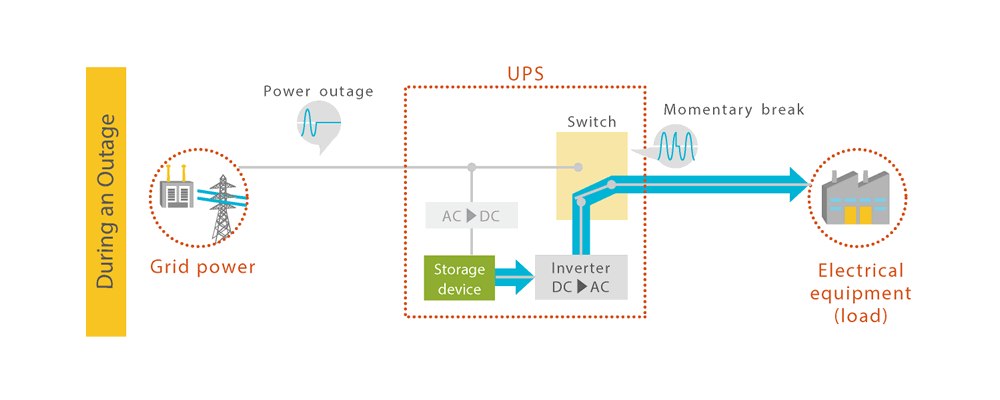
Under normal circumstances, that is, when commercial power is being supplied, the UPS supplies power to the equipment while charging the energy storage device. When the commercial power supply experiences a power outage, the commercial power supply is disconnected, and the DC power from the energy storage device is converted to AC power by Inverter and supplied to the electrical equipment. When this switchover is made, a momentary interruption occurs.
But why must the utility power be disconnected before powering the storage device?
If the power storage device were to output power without disconnecting the commercial power supply, not only would the power flow to the electrical equipment, but it would also flow back to the commercial power supply that is experiencing a power outage. This means that the commercial power supply needs to be disconnected, and time is required to switch to the power storage device.
Furthermore, the momentary interruption that occurs when the commercial power source is disconnected and the DC power of the energy storage device is connected can generate noise and cause electrical equipment to malfunction.
The advantages of Passive Standby are that the power consumption of the UPS itself is extremely low, and the circuit system is simple, compact, and inexpensive. This is because, under normal circumstances, commercial power is supplied directly to electrical equipment without power conversion. However, the disadvantage is that the voltage fluctuation is somewhat large when switching from commercial power to the power storage device.
In fact, because commercial power sources are subject to voltage fluctuations(*), electrical appliances used at home are generally designed to operate within a range of ±10% of the commercial power source. Recently, there have been many electrical appliances that can be used over a wide range of voltages, from 100 to 240V, so that they can be used overseas.
In summary, when using Passive Standby, it is assumed that the electrical equipment will function normally even if it is directly supplied with commercial power, allowing for a certain degree of voltage drop, disturbance in the voltage waveform, and momentary interruptions when switching power.
For this reason, they are rarely installed in power supply facilities that supply electricity, and small-capacity UPSs are often distributed to end-user electrical equipment.
* Based on the provisions of the Electricity Business Act and its Enforcement Regulations, the voltage must be maintained within 101±6V for a standard voltage of 100V and 202±20V for a standard voltage of 200V.
Written by: Toshiyuki Nishizawa, Senior Sales Engineer, Sales Division, SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
Update date: /release date: