



-
- Free Word Search




In the second lesson, we explained three types of power troubles: "momentary dip," "momentary interruption," and "blackout." However, in fact, we, the power receivers, can also cause power troubles without our knowledge. In the third lesson, we will learn about power troubles caused by the power receivers.
Power problems can occur depending on the type of electrical equipment used by the power receiving party. Let's divide electrical equipment into two main categories based on fluctuations in electricity usage.
Electrical devices such as household appliances, lighting, and computers consume a relatively stable amount of electricity. Because there are no major fluctuations in electricity consumption, it is easy for electric power companies to select the capacity, wiring, and tolerance of the power transmission equipment, making these electrical devices relatively easy to supply electricity to.
Electrical equipment for power systems such as elevators and trains repeatedly start and stop, and consume a large amount of electricity, so they require transmission equipment with large capacity, wiring, and durability. From the perspective of the power company that transmits the electricity, they can be said to be troublesome electrical equipment.
Electrical equipment with stable electricity usage does not experience any major problems, but power-driven electrical equipment with large fluctuations in electricity usage may affect the power transmission side. Next, we will explain power supply problems caused by power-driven electrical equipment.
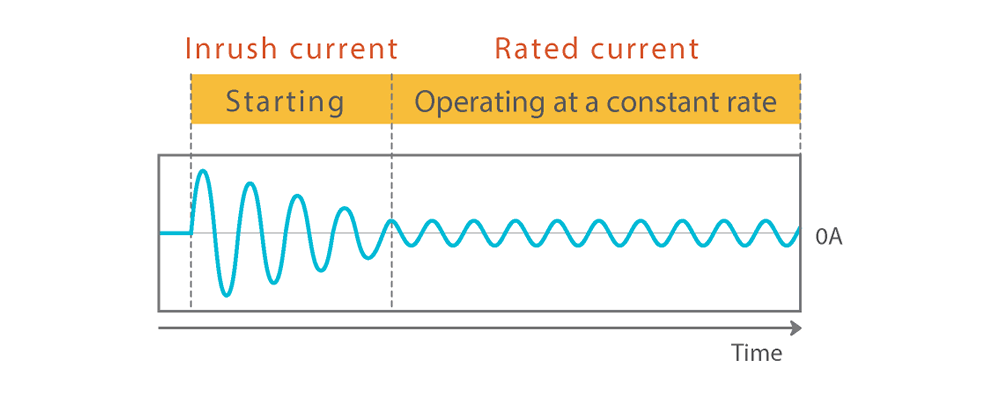
The moment a motor starts, it requires a large amount of electricity. This is called the "inrush current." When it is rotating at a constant speed after starting, it consumes a steady amount of electricity. This is called the "rated current." Since inrush current instantaneously consumes several to several tens of times the rated current, the power transmission equipment must also be prepared to handle the inrush current.
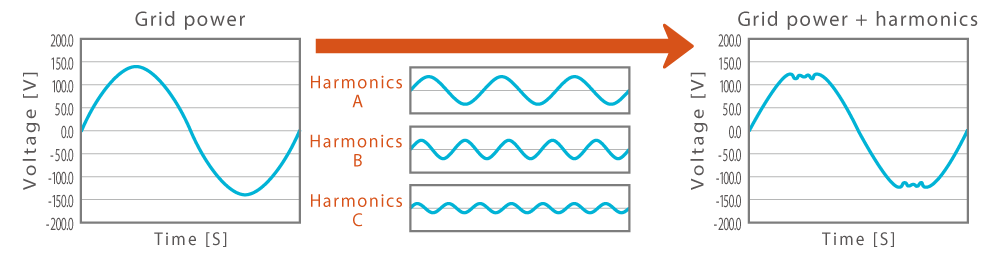
Harmonics are electrical noise generated by motors. Servomotors in particular are motors that are prone to generating harmonics. These harmonics have various effects on electrical equipment. When harmonics are generated from a motor, they flow into the power transmission side and can cause other electrical equipment in the factory to malfunction. In the worst case scenario, the harmonics can cause electrical equipment to heat up and burst into flames.
So far, we have learned about the circumstances of those who use electricity.
In order to avoid these power troubles on the power transmission and reception sides, power outage countermeasure devices are necessary to protect electrical equipment. Power supply devices will be selected by combining the "momentary drops," "momentary interruptions," and "power outages" introduced in the previous article with the types of electrical equipment discussed in this article. In the next article, we will learn together about the mechanisms and types of power outage countermeasure devices.
Written by: Toshiyuki Nishizawa, Senior Sales Engineer, Sales Division, SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
release date: