



-
- Free Word Search




Double Conversion Online is a system that constantly supplies electricity to electrical equipment through Inverter. It is such a reliable power supply system that the term UPS refers to Double Conversion Online.
Under normal circumstances, the UPS converts commercial AC power into DC power. The converted DC power is split into two, one to charge a power storage device, and the other to be converted back to AC by Inverter and supplied to electrical equipment. Even during a power outage, power is supplied via Inverter, so there is no need to switch power supplies, and there is no voltage fluctuation, allowing for uninterrupted power supply. Because it always passes through Inverter, it is a highly reliable power supply method.
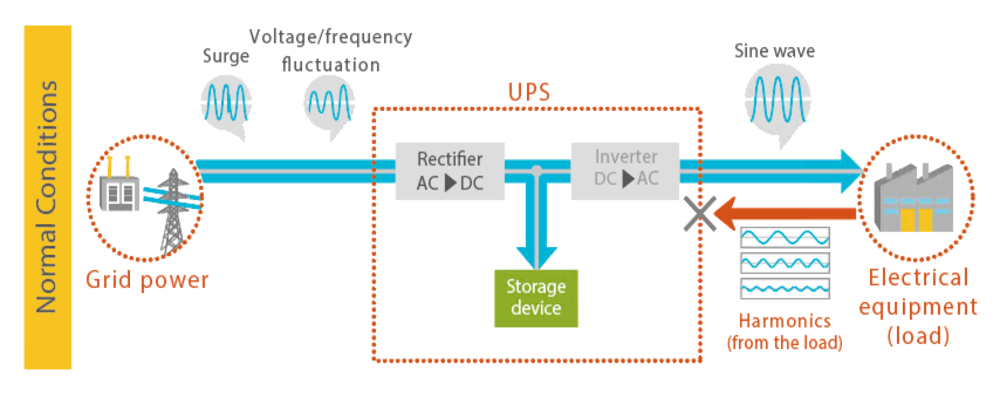
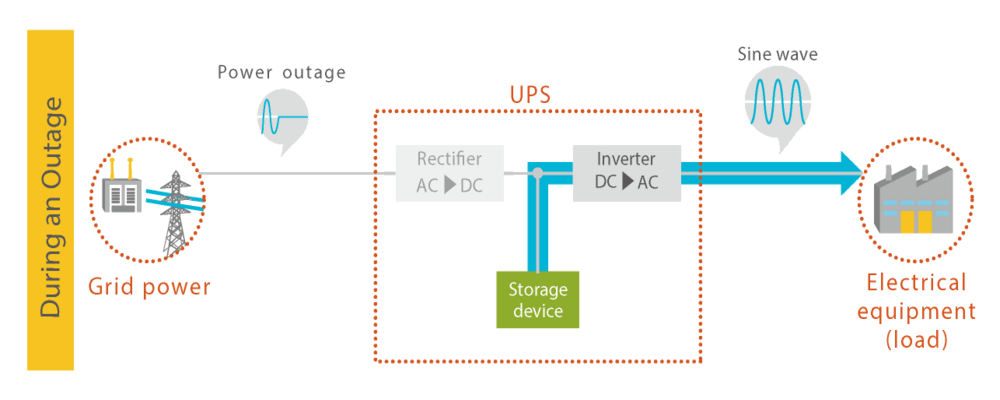
This method is also called the "double conversion method" because the power is converted twice, from AC to DC and from DC to AC. It is also called the "online method" because power is always supplied from Inverter line.
The advantage of Double Conversion Online is that it always passes Inverter, prepares it into clean electricity, and supplies it to electrical equipment, and can supply power without interruption even during a power outage. Unlike the "Passive Standby" introduced in the fifth lesson, there is no need to worry about electrical equipment stopping due to voltage fluctuations in the commercial power supply.
However, Inverter cannot handle large currents. When a large current such as an inrush current flows through Inverter, it switches from Inverter power supply to bypass operation (bypass power supply)*. If the waveforms of Inverter and commercial power supply are not synchronized at this time, a momentary interruption of about 50 to 300 ms occurs before they are synchronized. This momentary interruption may cause electrical equipment to stop or the switchover to fail. Therefore, it is necessary to select the rated capacity of the UPS according to the inrush current. In addition, since the power is converted twice, the power consumption is about 2 to 3 times higher than that of Passive Standby. Since there are many parts, the main unit is large and tends to be expensive.
Considering the above characteristics, Double Conversion Online is mainly used for backing up electrical equipment that requires "little power fluctuation and cannot tolerate any disturbance in the power waveform," and it can be said to be the method most commonly adopted in data centers and other places.
* Bypass operation (bypass power supply) is an operating mode in which commercial power is supplied directly to the UPS so that it can continue to power electrical equipment (loads) even when the UPS is undergoing maintenance or has an internal failure.
Written by: Toshiyuki Nishizawa, Senior Sales Engineer, Sales Division, SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
Update date: /release date: