



-
- Free Word Search




Airflow is the amount of air a fan moves, while static pressure is the force of air pushing against its surroundings when airflow is restricted or blocked. Higher static pressure allows a fan to move air through narrower or more resistant spaces.
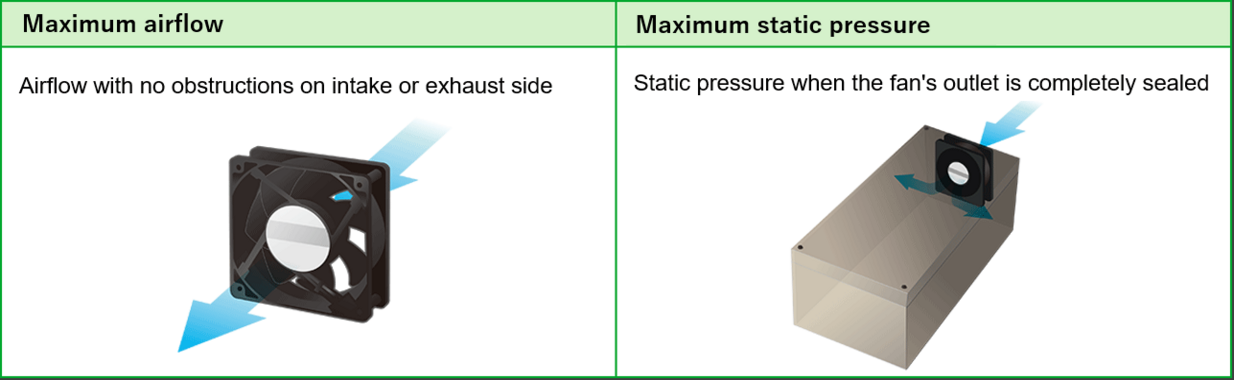
Maximum airflow is the volume of air a fan can deliver with no inlet or outlet obstruction.
Maximum static pressure is the pressure generated when airflow is completely blocked. Since neither situation occurs in real applications, a fan installed in a device will not achieve these maximum values.
So, what happens to airflow and static pressure when a fan is actually installed in a device?
When you look at the catalog, you'll see an airflow–static pressure characteristic curve alongside the fan specification table.
During actual operation, the airflow and static pressure settle at an operating point on the P-Q curve, determined by the system's resistance.
The "airflow–static pressure characteristic," also known as the "P–Q characteristic," describes fan performance.
Its curve varies depending on the fan type and model.
In this article, we’ll use a typical axial fan to explain how to interpret the P–Q curve.
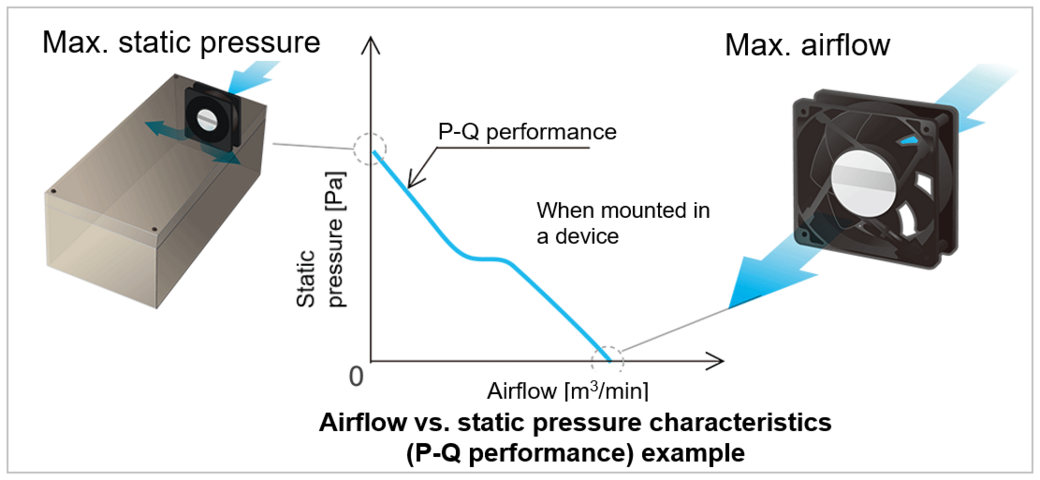
The airflow–static pressure characteristic curve shows that maximum airflow is observed when static pressure is 0 Pa, and maximum static pressure is observed when airflow is 0 m 3 /min. In an actual installation, the airflow and static pressure are typically found between the points of maximum airflow and maximum static pressure on the characteristic curve.
This curve also changes depending on the fan’s rotational speed. When multiple fans are installed together, they affect the overall airflow–static pressure characteristic of the system.
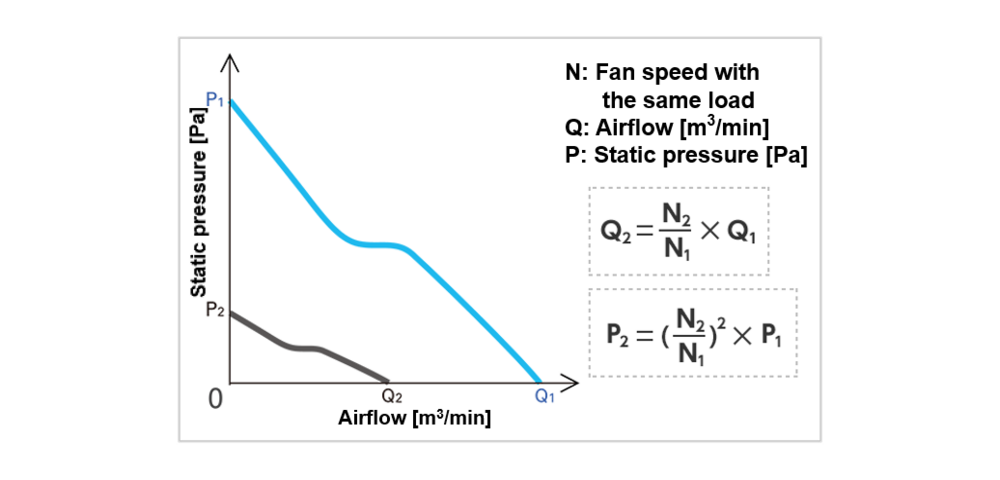
In general, a fan’s airflow is proportional to its rotational speed, while static pressure is proportional to the square of the speed. This means that doubling the fan speed produces approximately twice the airflow and four times the static pressure. Using this principle, the desired P–Q characteristic curve can be estimated from the current airflow and static pressure values.
When multiple fans are used, the overall airflow–static pressure characteristic depends on whether they are connected in series or in parallel. For instance, using two identical fans in series theoretically doubles the static pressure, while using them in parallel doubles the airflow.
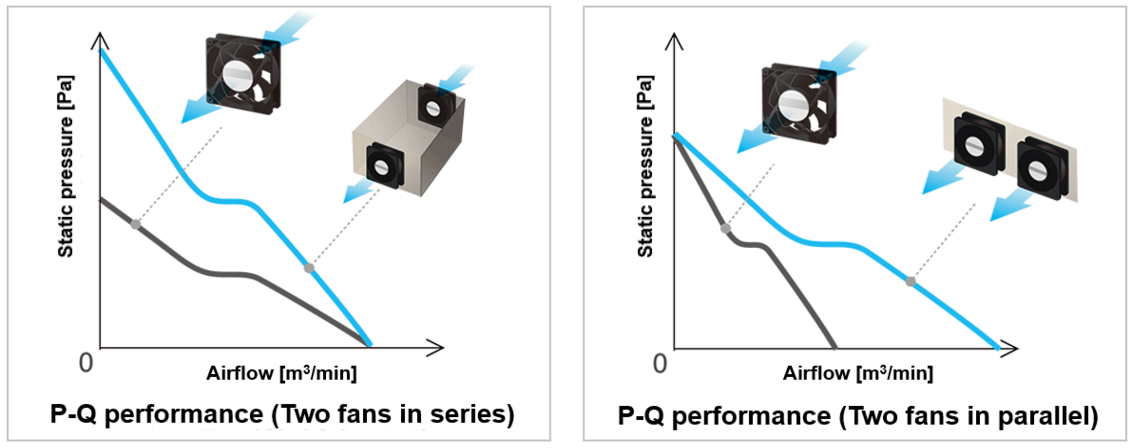
However, in actual systems, airflow interference between fans often reduces performance, preventing it from reaching theoretical values. Placing fans too close together increases interference, which often leads to performance falling well below the expected theoretical values.
Using multiple enclosures with built-in fans can significantly reduce the performance of lower-powered fans. For example, while enclosure A and B may each provide sufficient airflow on their own, combining them could cause the fan in enclosure A to become less effective due to airflow interference.
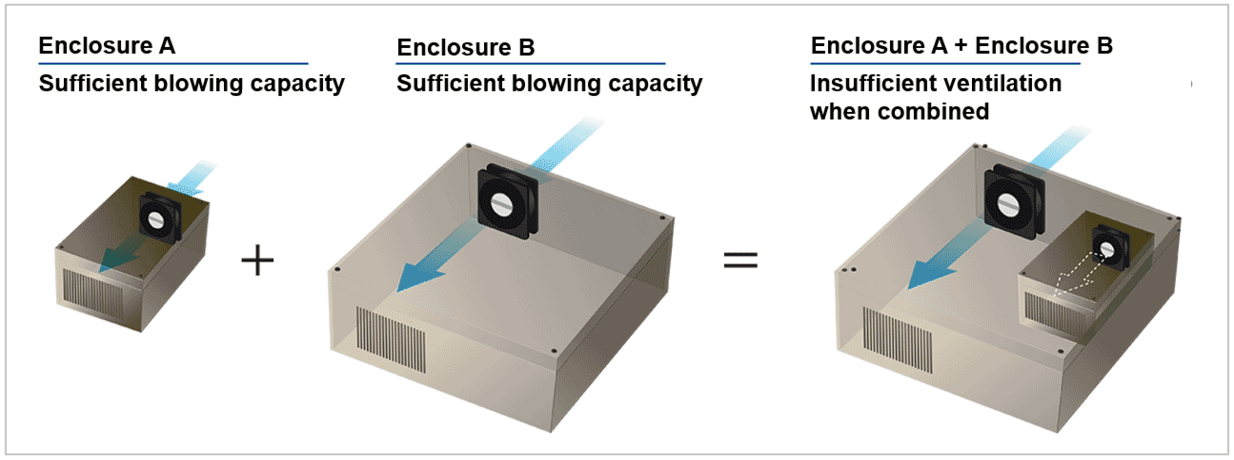
In devices with multiple components, thermal design is often pushed to the limit for each enclosure. This can lead to poor airflow in certain areas, leaving some parts without adequate cooling. Component layout can also affect fan performance, so it's important to carefully plan airflow and heat management during design.
The industry's first portable double chamber, developed by SANYO DENKI, is compact and lightweight, allowing it to be easily attached to large equipment that cannot be moved. This enables accurate measurements to be taken directly on-site.
Measurement is simple—just attach a duct to the air vent.
More details about the Airflow Tester are available in our downloadable materials.
Supervised by: SANYO DENKI CO., LTD. Cooling System Design Department
Update date: /release date: