



-
- Free Word Search




The PWM control function enables external regulation of fan speed through Pulse Width Modulation.This is achieved by adjusting the duty cycle of a pulse signal applied between the control pin and GND, allowing precise control of rotational speed.
By adjusting the airflow according to changes in the device’s heat generation (i.e., load conditions), the fan can provide optimal cooling only when needed. This enables efficient thermal management, reduces power consumption, and contributes to quieter system operation.
*Note: The explanation is based on examples from our products.
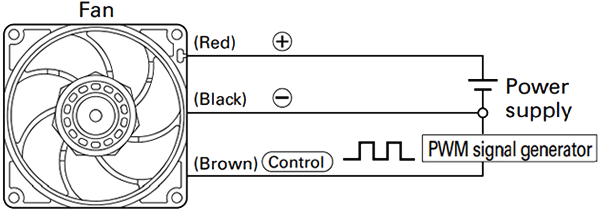
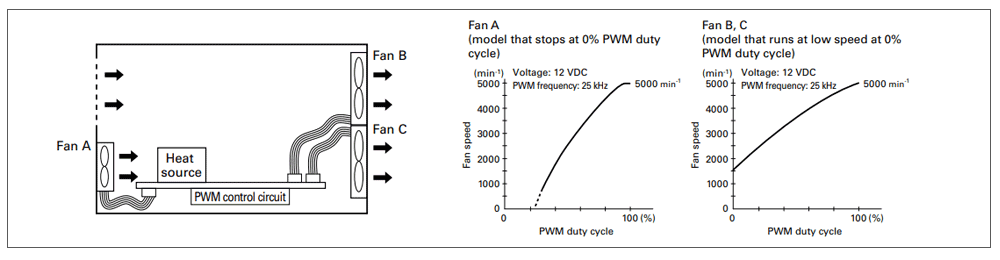
Fans with PWM control change their rotational speed according to the duty cycle of the input PWM signal, as shown in the characteristics below.
Users can define fan speed according to system requirements, enabling operation at the appropriate speed when needed.
Additionally, fan speed in response to PWM signals can be customized to meet user requirements. For example, the fan can be set to stop or operate at low speed when the duty cycle is 0%.
The following example shows fan characteristics based on a specification in which the fan stops when the PWM duty cycle is 0%. Specifications may vary depending on the model, so please contact us for details.
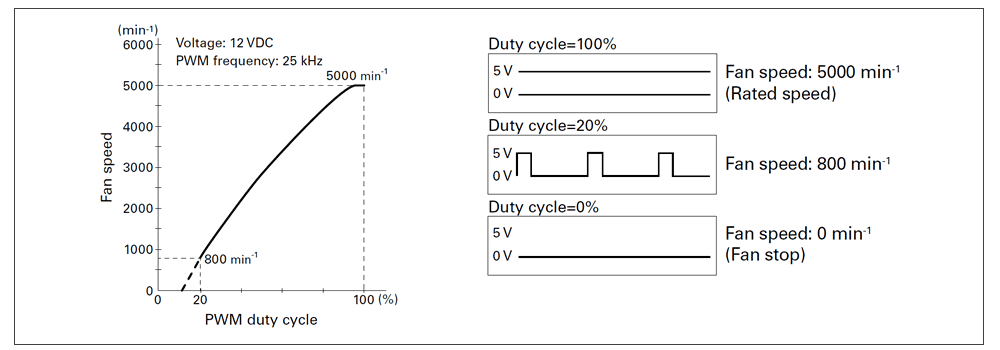
In the graph showing PWM duty cycle and fan speed, dashed or missing lines represent areas where the fan speed is not stable. In this example, that means duty cycles under 20%.
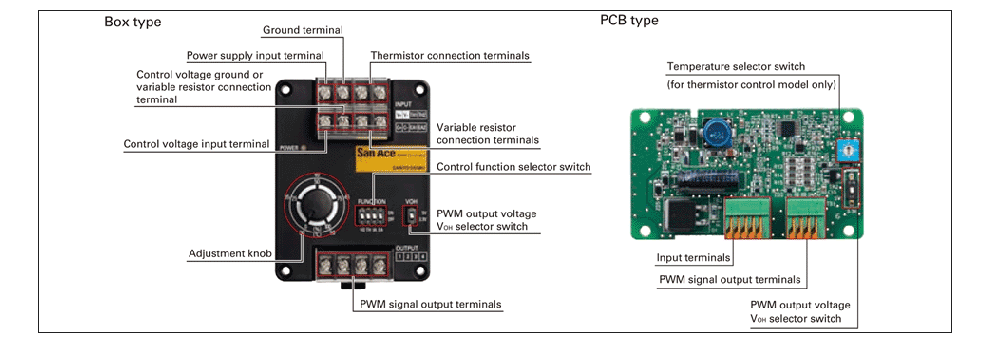
Implementing PWM control typically required custom circuit design. By using this product, users can easily integrate PWM-controlled fans without designing a new circuit, supporting energy-efficient and low-noise system operation.
Compatible with 12 V / 24 V / 48 V fan power supplies.
Up to four PWM-controlled fans can be connected and used.
Supports three control methods: voltage control, variable resistor control, and thermistor control.
The following are examples of applications using our PWM-controlled fans.
By combining a thermistor that detects air or component temperature within the equipment and a PWM control circuit, the fan with PWM control function can be regulated in response to temperature changes in the system.
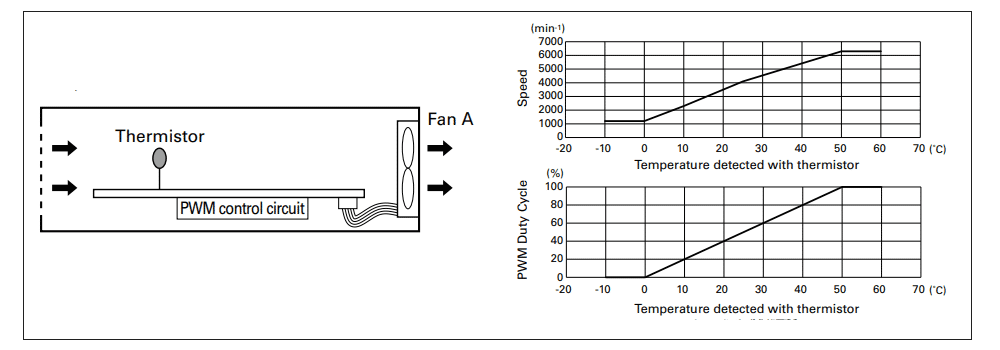
Since control is performed via digital PWM input, multiple fans can be controlled simultaneously regardless of fan type or input voltage.
As shown in the diagram, multiple fans with different PWM characteristics can be installed and controlled simultaneously within the equipment. This allows the system to adjust airflow according to changes in operating conditions, contributing to reduced power consumption and lower noise levels.
| mode | PWM Duty | Fan A | Fans B and C |
| Full operation | 100% | 5000 min-1 | 5000 min-1 |
| Normal operation | 60% | 3500 min-1 | 4000 min-1 |
| Standby (energy saving) | 0% | Stop | 1500 min-1 |
Company O, a manufacturer and supplier of security-related equipment including surveillance cameras, recently began developing a high-resolution Full HD outdoor surveillance camera system. However, the company faced several challenges related to thermal management within the device. Mr. T, the leader of Company O’s design and development team, explains:
“The new camera system we’re developing is equipped with a high-performance video processing engine, which generates a significant amount of heat inside the device,” explains Mr. T. “Initially, we considered using high-airflow fans, but their high rotational speed caused vibrations that led to image blurring. On the other hand, low-speed fans reduced vibration but couldn’t provide sufficient airflow to manage the heat effectively.”
As he continued gathering information, Mr. T came across the PWM Control function and found it intriguing.
“We found that with PWM-controlled fans, it’s possible to adjust the fan speed by simply inputting a pulse signal,” says Mr. T. “We expected this feature could also help solve the noise issue we were facing. Since the surveillance camera system operates outdoors 24/7, we thought we could reduce fan speed during cooler nighttime hours to minimize noise. We even considered developing our own PWM control circuit, but the required effort for designing a new board and the time needed for evaluation turned out to be more than we anticipated, so we had to abandon the idea.”
While continuing his research, Mr. T consulted a sales representative from SANYO DENKI about the challenges he was facing. Through this discussion, he was able to identify a potential solution.
“Initially, I consulted them about the vibration issues we were experiencing with our fans,” says Mr. T. “They proposed that simply replacing our existing fans with SANYO DENKI models could reduce vibration. I was intrigued by their detailed explanation, which included structural design features that minimize vibration, precise balancing during the manufacturing process, and high assembly accuracy. Since our surveillance camera system includes components that are sensitive to heat, the cooling fan plays a critical role. We had been struggling to balance image quality and system performance, but with SANYO DENKI’s DC Fans, we saw the potential to achieve both effective cooling and reduced vibration.”
Since the proposed fan included a PWM control function, I also brought up the controller circuit development we had previously abandoned,” Mr. T explains. “In response, the SANYO DENKI sales representative suggested a board-type PWM controller as a solution.
“I was impressed by how easy it was to use the San Ace PWM Controller—just connect it to the fan and it’s ready to go,” says Mr. T. “Thanks to the thermistor, which detects internal device temperature, the fan speed is automatically adjusted based on thermal conditions. As a result, we were able to reduce noise by an additional 30 dB during nighttime hours when less airflow is needed.”
Source: SANYO DENKI CO., LTD. Cooling System General Catalog Technical Information
release date: