
Fan Current
- Home
- Basic information for Knowledge fans
- Fan Current



When selecting a fan for use in a device, it’s important to consider how changes in electrical current—especially during startup or when the fan is blocked—can impact the system. In Lesson 5, we’ll take a closer look at fan current and its role in protecting your equipment.
Since fans are driven by motors, one key characteristic to consider is how the electrical current changes during operation. Immediately after the fan is powered on, the current starts at a high level, then gradually decreases until it stabilizes. In this section, we’ll explain the behavior of current in three stages: power-on, startup, and steady-state operation.
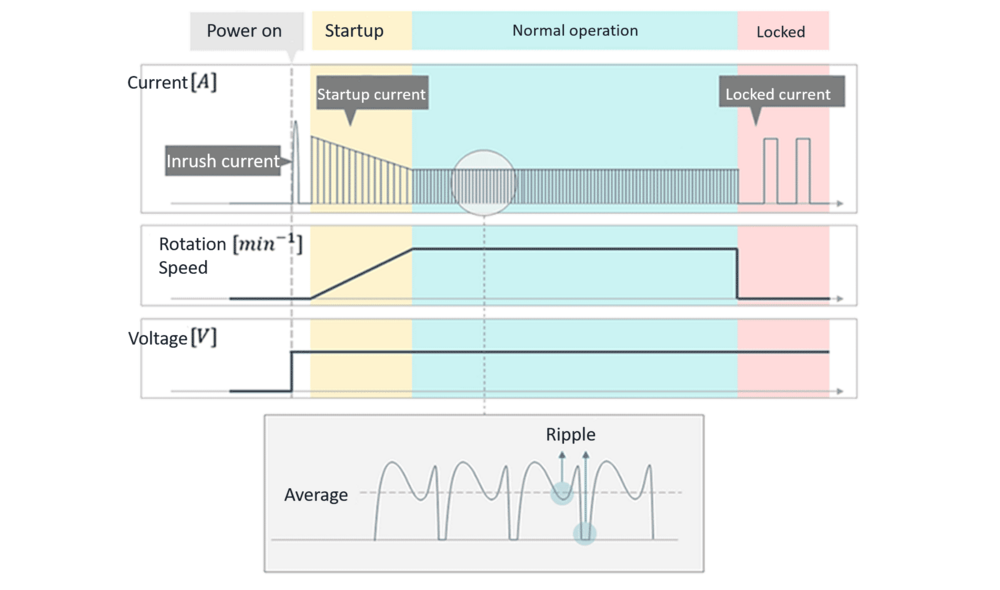
Fan drive circuits include components such as smoothing capacitors. As a result, when power is first applied, these capacitors begin charging all at once, causing a brief surge of high current. This sudden spike is known as inrush current.
Inrush current, determined by the fan’s drive circuit, is often the highest current observed during operation, but it quickly settles within a short time.
After the fan is powered on, a high peak current can occur even when the rotational speed is still low.
At SANYO DENKI, we refer to this as startup current.
It peaks immediately after startup and gradually decreases as the fan accelerates.
This is because the fan also functions as a generator during rotation, producing back electromotive force (back EMF), which increases with rotational speed.
The duration of startup current varies depending on the fan, but for most of our products, it typically lasts less than 10 seconds.
The current measured when the fan’s rotational speed has stabilized is called the rated current. Due to factors such as back EMF, the current during steady-state operation contains ripple. The rated current value listed in the catalog represents the average current including ripple. However, since the ripple occurs periodically and with consistent amplitude, it has minimal impact on the average value.
If a fan blade becomes obstructed due to external factors, a high current—similar to the initial startup current—may be generated. To prevent damage caused by prolonged exposure to this peak current, our products are equipped with a Locked Rotor Protection feature. For instance, in DC fans, this protection is implemented using a current cut-off method, which automatically cycles the fan on and off at regular intervals.
Supervised by: SANYO DENKI CO., LTD. Cooling System Design Department
release date: