



-
- Free Word Search




The word “fan” commonly brings to mind household appliances such as electric fans or ventilation fans. However, the “cooling fans” introduced here are installed inside equipment and serve the purpose of cooling the device itself. In recent years, cooling fans have also been increasingly used for purposes beyond cooling, such as ventilation and air circulation.
Cooling fans are typically categorized by the type of power supply they use and their structural form.
There are two main types of power input for cooling fans: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). These are commonly referred to as AC fans and DC fans. When classified by shape, cooling fans generally fall into three categories: Axial Fans, Centrifugal Fans, and Blowers.
When browsing products, a name like “DC Axial Fan” indicates an axial fan powered by a DC input. Of course, naming conventions may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, but the classification itself is generally consistent.
Related article: Knowledge "2nd Period: Types of Fans"
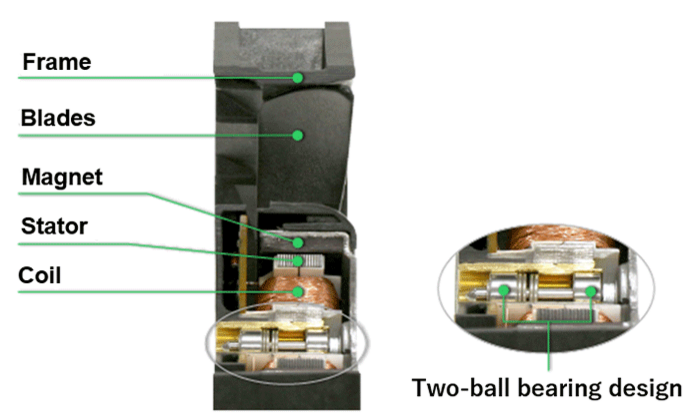
Figure 1: Cross-section of a fan
The structure of the fan will be explained using a cross-sectional illustration.
Cooling fans typically consist of components as shown in Figure 1, with the ball bearing being especially critical.
SANYO DENKI uses a two-ball bearing design across all fan models. This reduces the load on the bearings, leading to enhanced reliability and longer lifespan.

Figure 1: Cross-section of a fan
Related article: Knowledge "3rd Lesson: Fan Lifespan"
To adjust the rotational speed of a fan, the PWM control function can be used. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) regulates the fan speed by varying the width of the control signal pulses, offering broader and more precise control compared to voltage-based methods.
Controlling fan speed via PWM requires a circuit that can generate PWM signals. For users who prefer not to design their own circuits, SANYO DENKI’s “PWM Controller” offers a convenient solution. In addition, the “San Ace Controller” enables remote fan speed management through IoT technology.
When a fan generates noise after being installed in a device, it may be due to physical contact between the fan and the equipment during rotation. One solution is to use vibration-absorbing materials such as rubber mounts. Another possible cause is resonance between the fan and the device. In that case, increasing the rigidity of the equipment can help prevent resonance with the fan’s rotational speed.
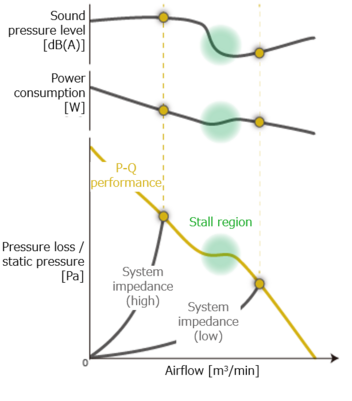
Figure 2: Example of ventilation resistance and air volume - static pressure characteristics
If the abnormal noise is coming from the fan unit itself, it is typically due to one of three main factors.
Wind noise: Caused by air displacement due to rotating blades.
Electromagnetic noise: This is primarily caused by switching operations within the motor.
Mechanical noise: This type of noise occurs when the rotor is unbalanced, causing vibrations during rotation.
These types of noise are determined during the fan manufacturing process. Wind noise, however, can be reduced by adjusting the rotational speed using features such as PWM control. Since the sound pressure level of a fan varies depending on its speed, setting the fan to operate at the lowest-noise speed is ideal. However, reducing the speed also affects airflow, making it challenging to balance cooling performance and noise reduction.
Therefore, if you aim to reduce noise while maintaining optimal cooling performance, the best approach is to select a fan based on the airflow–static pressure characteristics that match the ventilation resistance of the equipment. This helps identify the optimal operating point for the fan.

Figure 2: Example of ventilation resistance and air volume - static pressure characteristics
Related article: Knowledge "7th lesson: Ventilation resistance of equipment"
What is the method for quantifying airflow when a fan is installed in a device?
What is an "ACDC Fan" that achieves the performance of DC Cooling Fan with AC power?
What is a "Centrifugal Fan" that reduces the number of fans while improving cooling performance?
High static pressure "Oil Proof Fan" ensures cooling performance even in harsh factory environments
release date: