



-
- Free Word Search




Fan noise is an important consideration for devices used in quiet environments, and its level can vary depending on the arrangement of internal components. Section 6 discusses fan noise in settings without nearby obstacles.
Fan noise is measured in dB(A), which represents sound pressure levels adjusted to reflect human hearing sensitivity. The A-weighting scale, as defined by JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), accounts for the fact that certain frequencies are more easily perceived than others.
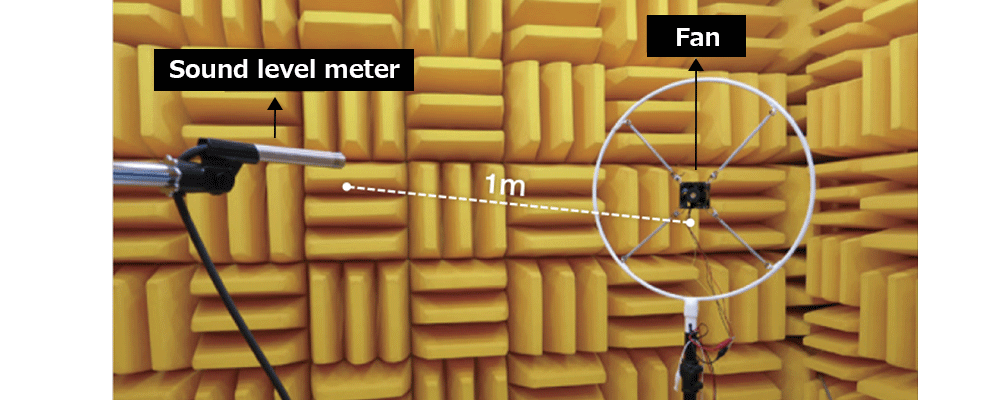
Sound pressure levels are measured in an anechoic chamber using a sound level meter placed 1 meter from the fan’s inlet side. To minimize interference from surrounding objects, the fan is suspended in mid-air during testing. This setup ensures accurate measurement of noise levels when the fan operates at maximum airflow.
Formula 1 describes the relationship between sound pressure level and fan rotational speed, while Formula 2 is used to calculate the combined noise level when multiple sound sources are present.
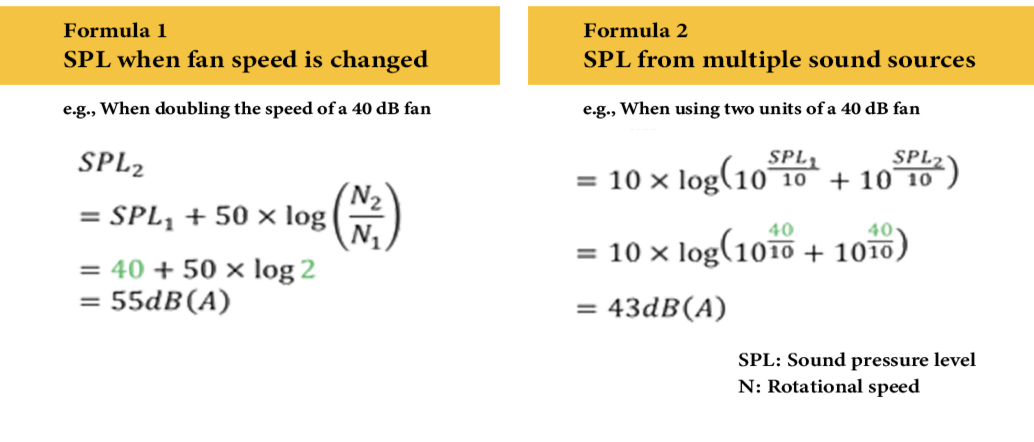
To double the maximum airflow, there are two possible approaches: increasing the fan’s rotational speed or adding an additional fan. However, as shown in the formulas above, these two methods result in significantly different sound pressure levels. Therefore, using two fans is generally more effective for reducing noise. This highlights how adjusting the number and speed of fans can be an effective strategy for minimizing noise in device design.
Supervised by: SANYO DENKI CO., LTD. Cooling System Design Department
release date: